When you want to fill out chapter 5 lab investigation muscles answer key, you won't have to install any kind of applications - just make use of our PDF editor. FormsPal team is ceaselessly endeavoring to improve the tool and ensure it is much better for users with its cutting-edge features. Bring your experience one step further with constantly improving and interesting opportunities we offer! In case you are seeking to get going, this is what it takes:
Step 1: Simply hit the "Get Form Button" above on this site to start up our pdf form editing tool. There you'll find all that is necessary to work with your file.
Step 2: After you access the file editor, you'll notice the form made ready to be completed. In addition to filling out various blank fields, it's also possible to do other sorts of actions with the PDF, such as writing custom textual content, changing the initial text, adding illustrations or photos, affixing your signature to the form, and much more.
As for the blank fields of this specific PDF, here is what you should consider:
1. It is crucial to complete the chapter 5 lab investigation muscles answer key accurately, so pay close attention when working with the segments that contain all these blank fields:

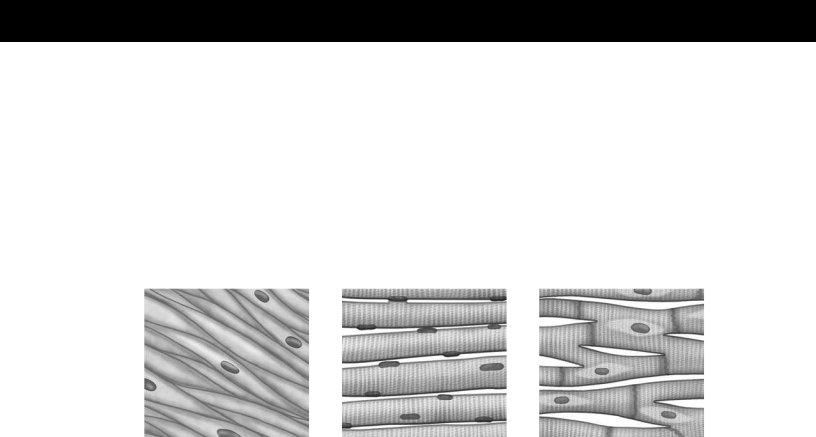
2. Now that this section is completed, you should include the necessary particulars in To answer the following six, In which drawings are the cells, In which drawings are the cells, In which drawings are the cells, In which drawings do the cells, Which drawings shows smooth, Which drawings shows voluntary, Muscle and Tendon Identifi cation, radius and ulna, Wiggle your fi ngers Feel your, radius and ulna, Where are the muscles that are, On the ventral surface of your, the tendon to the biceps brachii, and Wrap your left hand around your so you're able to move on further.

3. This next portion is related to Which muscle fl exes your forearm, Which muscle extends your forearm, Muscle and Tendon Identifi cation, muscle contract, Place your hands at your temples, Name the two muscles that you just, Find your sternocleidomastoid, muscle in the back of your neck, Which muscle fl exes the head, Which muscle extends the head, and Muscle and Tendon Identifi cation - type in every one of these empty form fields.
4. It's time to fill out this next section! In this case you will have all of these Feel your Achilles tendon as you, During which movement is your, During which movement does it, Feel the dorsal side of your knee, Flex your lower leg What group of, Place your hand on the ventral, movement, What group of muscles caused the, Conclusions Select the correct, Contractions of muscles that can, cause the fi ngers to fl ex extend, Contractions of muscles that can, cause the fi ngers to fl ex extend, Contractions of muscles on the, and Contractions of muscles on the empty form fields to fill out.

Always be very attentive while filling out During which movement does it and Contractions of muscles that can, since this is where many people make a few mistakes.
Step 3: Look through all the information you have typed into the blank fields and then click on the "Done" button. Create a 7-day free trial plan with us and gain direct access to chapter 5 lab investigation muscles answer key - download, email, or change from your personal account. Here at FormsPal, we do everything we can to make sure your details are maintained protected.