General Instructions
Section references are to the Internal Revenue Code unless otherwise noted.
Future developments. For the latest information about developments related to Schedule M (Form 990), such as legislation enacted after the schedule and its instructions were published, go to www.irs.gov/Form990.
Note: Terms in bold are defined in the Glossary of the Instructions for Form 990.
Purpose of Schedule
Schedule M (Form 990) is used by an organization that files Form 990 to report the types of noncash contributions received during the year by the organization and certain information regarding such contributions. The schedule requires reporting of the quantity and the reported financial statement amount of noncash contributions received by type of property. Report noncash donated items even if sold immediately after received. Don’t report noncash contributions received by the organization in a prior year. Don’t report donations of services or the donated use of facilities, equipment, or materials donated.
Who Must File
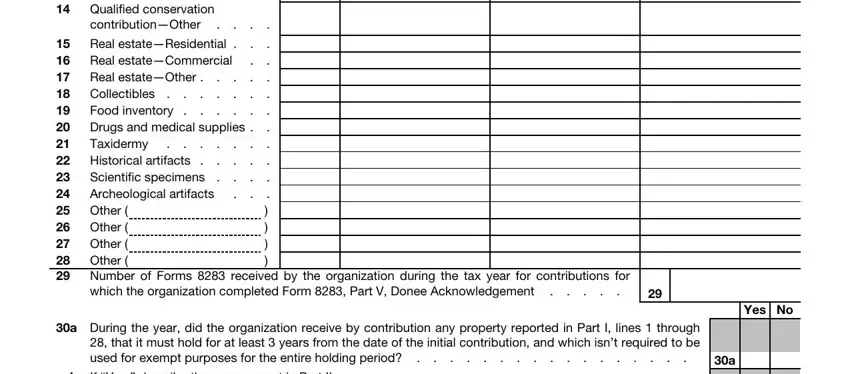
An organization that answered “Yes” to Form 990, Part IV, lines 29 or 30, must complete Schedule M (Form 990) and attach it to Form 990. This means an organization that reported more than $25,000 of aggregate noncash contributions on Form 990, Part VIII, line 1g, or that during the year received contributions of art, historical treasures, or other similar assets, or qualified conservation contributions, regardless of whether it reported any revenues for such contributions in Part VIII.
If an organization isn’t required to file Form 990 but chooses to do so, it must file a complete return and provide all of the information requested, including the required schedules.
Specific Instructions
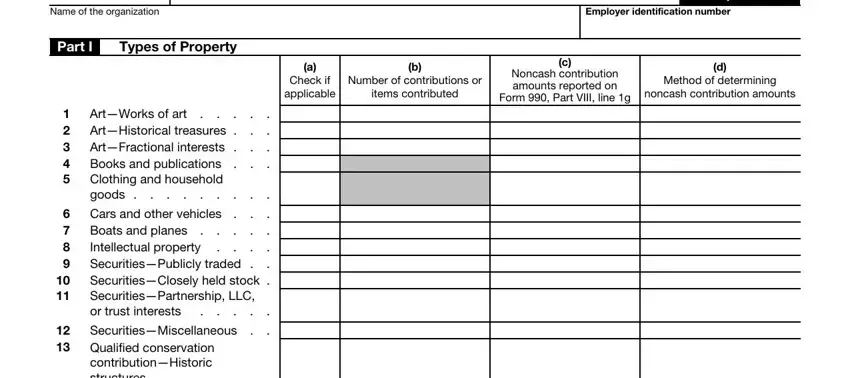
Part I. Types of Property
Column (a). Check the box if during the year the organization received any contributions of the property type identified.
Column (b). For each type of property received during the year, enter the number of contributions or the number of items contributed, determined in accordance with the organization’s recordkeeping practices. Explain in Part
IIof this schedule whether the organization is reporting the number of
contributions or the number of items received, or a combination of both methods. As described below, for contributions of securities, such as publicly traded stock, treat each separate gift (rather than each share received) as an item for this purpose.
Organizations that receive contributions of books, publications, clothing, and household goods aren’t required to complete column (b) for those items reported on lines 4 and 5.
Columns (c)–(d). In column (c), enter the revenues reported on Form 990, Part VIII, line 1g, for the appropriate property type. If none were reported, enter “0.”
In column (d), describe the method
used to determine the amount reported on Form 990, Part VIII, line 1g (for example, cost or selling price of the donated property, sale of comparable properties, replacement cost, opinions of experts, etc.). See Pub. 561, Determining the Value of Donated Property, for more information.
Example 1. A used car in poor
condition is donated to a local high school for use by students studying car repair. A used car guide shows the dealer retail value for this type of car in poor condition is $1,600. However, the guide shows the price for a private party sale of the car is only $750. The fair market value of the car is considered to be $750, which is the amount the organization reported on Form 990, Part VIII, line 1g. In column (c), the organization should enter $750. In column (d), the organization should enter “sale of comparable properties and/or opinion of expert” as the method used to determine fair market value.
Example 2. An organization primarily receives bulk donations of clothing, household goods, and other similar items, intended for resale. Under its permitted financial reporting practices, it doesn’t recognize or record revenue at the time of receipt of the contribution, but instead records such items in inventory and reports contribution revenues at the time of sale based on prior inventory turnover experience. In column (c), the organization can enter the amount that represents the total estimated amount of annual sales revenue for each type of property received under its permitted financial reporting method, and in column (d), enter “resale value or annual sales revenue” as the method of determining revenue.
Museums and other organizations that don’t report contributions of art, historical treasures, and other similar items as revenue, as permitted under generally accepted accounting principles,
enter “0” in column (c) and leave column
(d)blank. The organization can explain in Part II that a zero amount was reported on Form 990, Part VIII, line 1g, because the museum did not capitalize its collections, as allowed under Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification 958-360-25 (ASC 958-360-25).
An organization that received qualified conservation contributions or conservation easements must report column (c) revenue consistent with how it reports revenue from such contributions in its books, records, and financial statements. The organization must also report revenue from such qualified conservation contributions and conservation easements consistently with how it reports such revenue in Form 990, Part VIII.
Line 1. Works of art include paintings, sculptures, prints, drawings, ceramics, antiques, decorative arts, textiles, carpets, silver, photography, film, video, installation and multimedia arts, rare books and manuscripts, historical memorabilia, and other similar objects. Works of art don’t include collectibles reported on line 18 or taxidermy reported on line 21.
Line 2. An historical treasure is a building, structure, area, or property with recognized cultural, aesthetic, or historical value that is significant in the history, architecture, archeology, or culture of a country, state, or city.
Line 3. A contribution of a fractional interest in art is a contribution, not in trust, of an undivided portion of a donor’s entire interest in a work of art. A contribution of the donor’s entire interest must consist of a part of each substantial interest or right the donor owns in such work of art and must extend over the entire term of the donor’s interest in the property. A gift generally is treated as a gift of an undivided portion of a donor’s entire interest in property if the donee is given the right, as a tenant in common with the donor, to possession, dominion, and control of the property for a portion of each year appropriate to its interest in such property. For each work of art or item, report in column (b) the fractional interest for each year an interest in the property is received for the underlying work of art or item. See section 170(o) for special rules for fractional gifts.
Line 4. Enter information about contributions of all books and publications. Don’t include rare books and manuscripts reported on line 1, collectibles reported on line 18, and archival records reported on lines 25 through 28.