The exploration of Biochemistry Basics serves as a foundational pivot point in understanding the intricate relationship between biology and chemistry, essential for advanced studies in the biological sciences. It delves into the significance of atomic and molecular structures within biological organisms, illustrating how these structures dictate the characteristics and functionalities of living matter. By examining key concepts such as polarity, acidity, and basicity of molecules, students are equipped with the tools needed to decipher the molecular essence of life. The form introduces molecular modeling through various representations - ball-and-stick models, Lewis structures, and line drawings, offering a visual comprehension of molecular shapes and the types of bonds formed by atoms like carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Additionally, it ventures into the properties of biological molecules, distinguishing between polar (hydrophilic) and nonpolar (hydrophobic) entities, and extending the discussion to the solubility principles, functional groups, and the acidity or basicity of molecules. This comprehensive approach not only bridges the gap between chemistry and biology but also enriches the student's understanding of how microscopic molecular interactions manifest into macroscopic biological features and processes.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Form Name | Biochemistry Basics Form |
| Form Length | 8 pages |
| Fillable? | No |
| Fillable fields | 0 |
| Avg. time to fill out | 2 min |
| Other names | biochemistry basics what concepts from chemistry are helpful in studying biology answers, biochemistry basics answer key pogil, biochemistry basics answer key, biochemistry basics worksheet |
Biochemistry Basics
What concepts from chemistry are helpful in studying biology?
Why?
Typically chemistry is a prerequisite course for advanced biology courses. This is because everything in your body, everything in a plant, everything in a virus, etc. is made of atoms. The structures and properties of the molecules in an organism determine the features and properties of the organism. Which molecules are polar, which are nonpolar? Which molecules have acidic properties, which have basic prop- erties? A quick review of these concepts at the beginning of your advanced biology course will help you to understand the molecular basis for life.
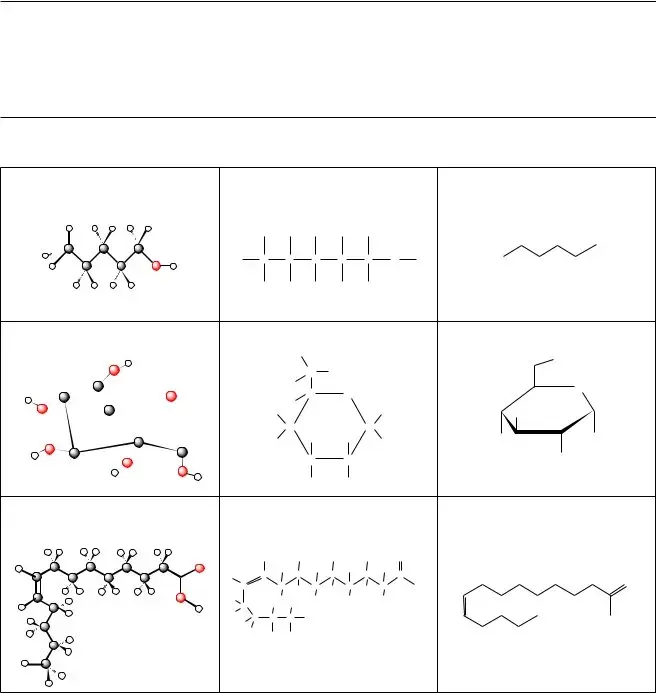
Model 1 – Molecular Drawings
Lewis structure of |
Line drawing of |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
H |
H |
|
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
H C |
C |
C C |
C O H |
H3C |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
H |
H |
H |
|
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
Lewis structure of glucose |
|
Line drawing of glucose |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
C |
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HO |
|
OH |
|
H |
|
OH |
HO |
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
C |
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lewis structure of unsaturated |
Line drawing of unsaturated |
||||||||||||
unsaturated fatty acid |
fatty acid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
fatty acid |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
H |
H |
|
H |
|
H |
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
C |
H |
C |
H |
C |
H |
C |
|
|
|
|
H |
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
O |
||||
|
|
C |
|
C |
|
C |
|
C |
OH |
|
|
||
|
C |
|
H |
H |
H |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
H |
|
H H H |
H |
|
H |
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H C |
C |
C |
C |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CH3 |
OH |
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
H |
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1.Name the three molecules that are illustrated in Model 1.
2.Name the three types of drawings that are used to illustrate the molecules in Model 1.
Biochemistry Basics |
1 |
3. How many bonds are typically formed by each of the following atoms:
Carbon |
Hydrogen |
Oxygen |
4.Which types of drawings in Model 1 provide more accurate images of the shape of a molecule? Justify your reasoning.
5.Refer to Model 1.
A. Symbols or atoms of what element(s) are missing from the line drawings?
B. In reading a line drawing, how do you know where atoms of these elements are in the struc- ture if they are missing from the drawing?
6.Locate the carbon and hydrogen atoms in the line drawing of isoleucine shown below and draw them in as if the drawing were a Lewis structure.
CH3 O
H3C
OH
NH2
Isoleucine
7.Isopropyl alcohol is a
8.If you were asked to write the chemical formula for one of the compounds in Model 1, which type of the drawing would be the easiest to use? Justify your reasoning.
9.What is the advantage to a scientist in using a line drawing rather than a
2 |
POGIL™ Activities for AP* Biology |
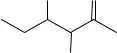
Model 2 – Properties of Biological Molecules
|
Polar Molecules |
|
|
|
Nonpolar Molecules |
||||
|
(hydrophilic) |
|
|
|
(hydrophobic) |
|
|||
Acidic |
|
|
O |
|
Acidic |
|
|
|
O |
|
H3C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
H3C |
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Lactic acid |
|
|
|
|
Fatty acid |
|
||
Neutral |
|
|
O |
|
Neutral |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CH3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H3C |
CH3 |
|
H3C |
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
CH3 |
|
|
|
NH2 |
|
|
|
|
CH3 |
CH3 |
|
Valine (amino acid) |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
O H |
HO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH H |
H |
|
|
|
|
Cholesterol |
|
|
|
HO |
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Glucose |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
CH |
|
CH |
CH |
|
|
|
|
|
H C |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
H |
|
O OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
OH H |
H |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
HO |
O |
O |
|
|
H |
|
|
CH |
|
OH H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
H |
|
OH |
|
|
Vitamin A |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
H |
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
H |
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lactose |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
OH |
H |
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HO |
|
|
|
N |
|
|
|
CH3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
CH3 |
|
|
CH3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adrenaline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
HO |
|
|
|
NH2 |
O |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Testosterone |
|
HO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dopamine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
NH2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
NH |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adenine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Biochemistry Basics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
10.Consider the polar molecules in Model 2.
A. In general, the presence of atoms of what element(s) makes a molecule polar?
B. What property do atoms of these elements have that helps make the molecules they are in polar?
C. Can nonpolar molecules also have atoms of these elements? If yes, what distinguishes a non- polar molecule from a polar molecule?
11.In chemistry there is a saying “like dissolves like,” which means things will mix with or dissolve into each other best when their polarities are similar.
A. Is water polar or nonpolar?
B. Is oil polar or nonpolar?
C. Which of the substances in Model 2 would dissolve well in water? Justify your reasoning.
D. Which of the substances in Model 2 are more likely to dissolve well in oil? Justify your reasoning.
E. Which class of substances in Model 2, polar or nonpolar, is more likely to be found in high concentrations in the bloodstream of a vertebrate? Justify your reasoning.
12.Refer to Model 2.
A. What is another term for a polar molecule?
B. What is another term for a nonpolar molecule?
C. Give the literal translation for the terms you gave in parts A and B above.
4 |
POGIL™ Activities for AP* Biology |
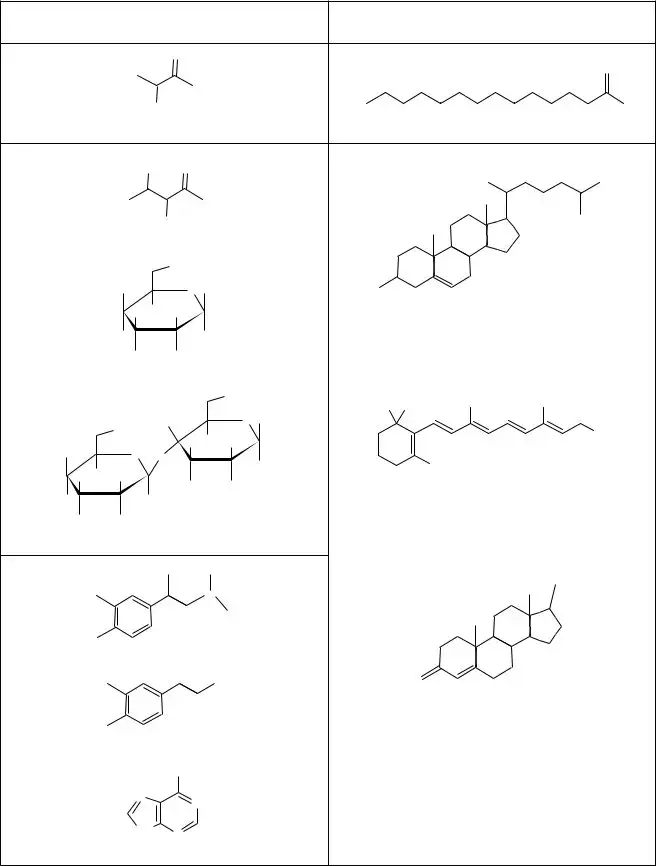
13.Functional groups are key groups of atoms in biological molecules. Describe the carboxyl func- tional group that both acidic molecules in Model 2 have in common.
14.Recall the definition of an acid that you learned in chemistry. Explain how the reaction below illustrates the acidic properties of lactic acid.
OO
H3C
OH
OH + H2O |
|
H3C |
|
|
|
O– |
+ H3O+ |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH
Lactic acid |
Lactate ion |
15.Describe the functional group, called an amine group, that the basic molecules in Model 2 all have in common?
16.Recall the definition of a base that you learned in chemistry. Explain how the reaction below illustrates the basic properties of adrenaline.
OH |
H |
|
HO |
N |
HO |
|
CH3 |
|
|
+ H2O |
|
|
|
|
HO |
|
HO |
|
|
Adrenaline
H
+ |
|
|
|
N |
|
CH3 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
H |
+ |
OH– |
|
|
|
|
|
17.Predict the approximate pH (pH = 7, pH > 7 or pH < 7) of fairly concentrated aqueous solu- tions of the following compounds from Model 2.
Lactic acid |
____________ |
Dopamine |
____________ |
Amino acid |
____________ |
Lactose |
____________ |
Biochemistry Basics |
5 |
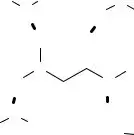
18.In chemistry you learned that covalent bonds are one type of intramolecular bond. They occur between nonmetal atoms in a molecule. You may have also learned about a type of intermo- lecular bond called a hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds are weak attractive forces between polar molecules containing strong polar bonds such as
H O H H O H
H O
N 
 H
H
H O
O H
H H  O H
O H
A. Label at least two covalent bonds in the diagram above.
B. Label at least one hydrogen bond in the diagram above.
19.Which of the molecules in Model 2 would form hydrogen bonds with itself (that is, other mol- ecules of the same type) or with water molecules if in a solution?
6 |
POGIL™ Activities for AP* Biology |
Extension Questions
20.Although amino acids have “acid” in their name, some are acidic in water solutions, some are basic, and others are neutral. Propose an explanation for this observation based on the structures and descriptions of the amino acids below.
Neutral amino acids
OO
H3C
OH HO OH
NH2NH2
Acidic amino acid |
|
Basic amino acid |
|||||||||||
O |
|
O |
|
|
O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H2N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
HO |
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
OH |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
NH2 |
|
NH |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
21.The structure shown below is a line drawing of noncyclic AMP, an important messenger mol- ecule in molecular communication systems.
A. Draw the missing carbon and hydrogen atoms on the molecule.
|
|
|
|
NH2 |
|
|
|
|
N |
N |
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
O P |
O |
N |
N |
➾ |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH OH
B. Write the chemical formula for a molecule of noncyclic AMP.
Biochemistry Basics |
7 |
22.The phosphate functional group in the noncyclic AMP molecule of Question 21 contains “acidic hydrogens.”
A. Explain what this phrase means.
B. Draw the noncyclic AMP molecule after it has dissolved in water.
8 |
POGIL™ Activities for AP* Biology |
