Each step in completing the critical incident report form captures details that ensure the participant receives appropriate care and that all regulatory requirements are met. This approach helps maintain high standards of safety and accountability in HCBS programs.
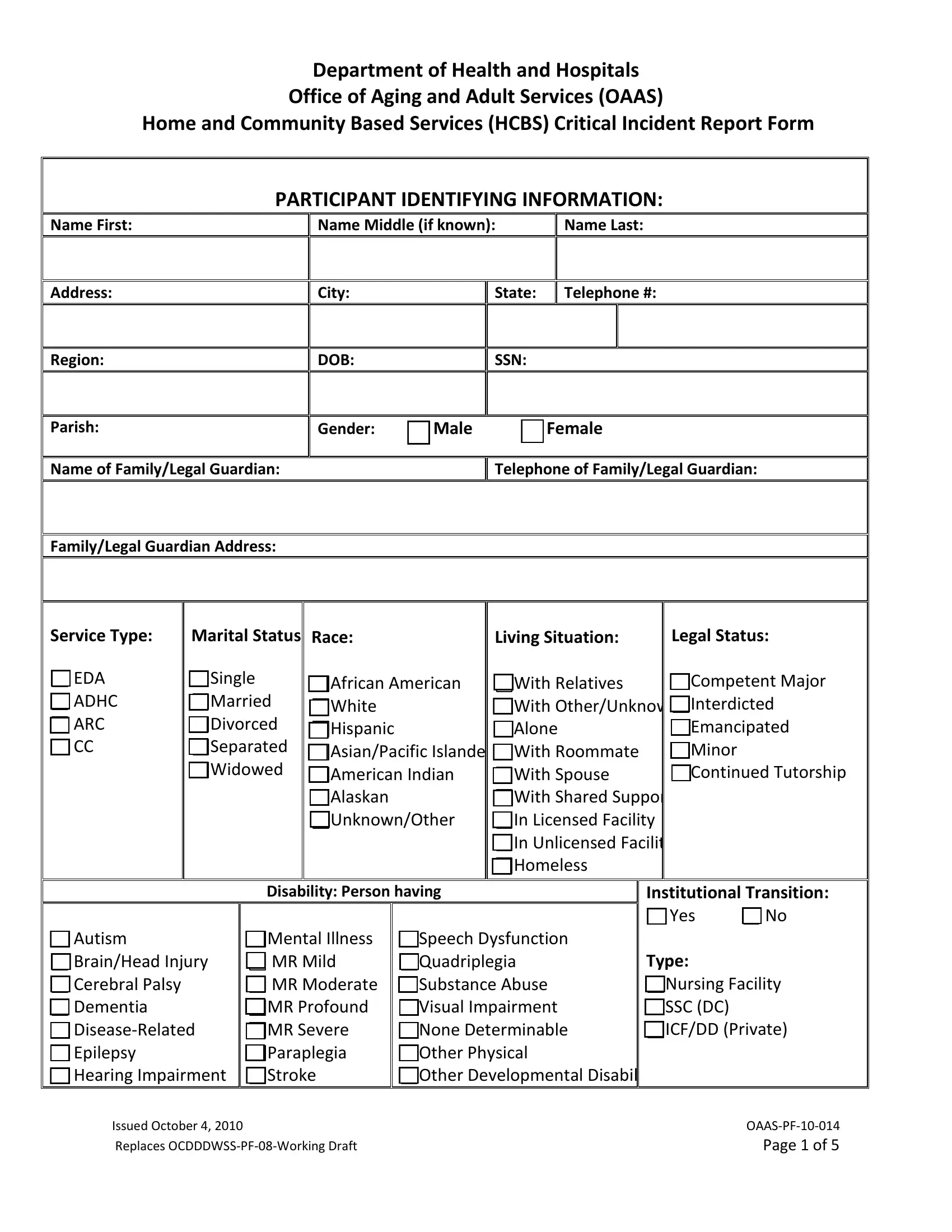
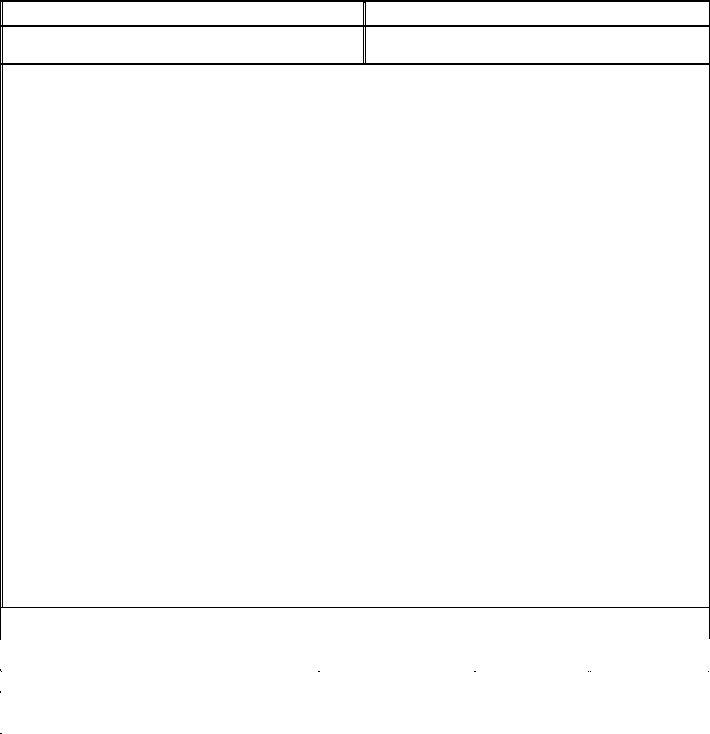
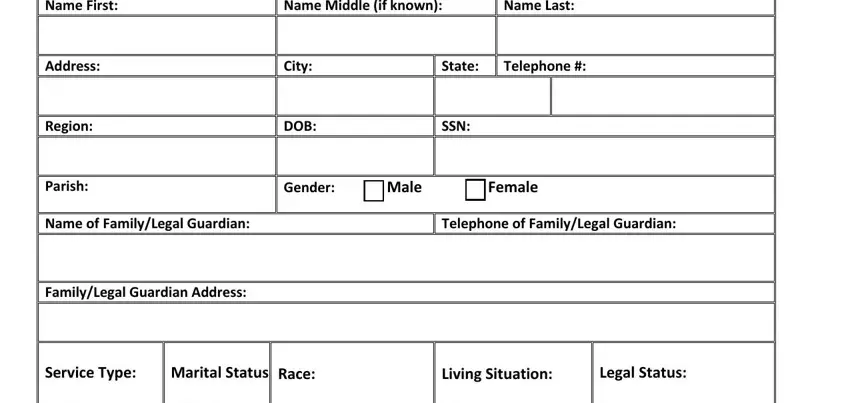
1. Collect Participant Identifying Information
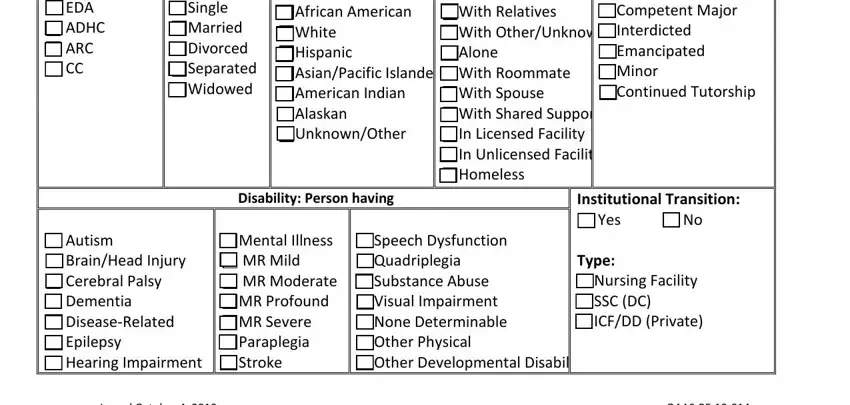
Enter the participant's full name, including first, middle (if applicable), and last names. Record the participant's address, city, state, and telephone number. Additionally, include details such as date of birth, social security number, gender, and the name and contact information of any family or legal guardian.
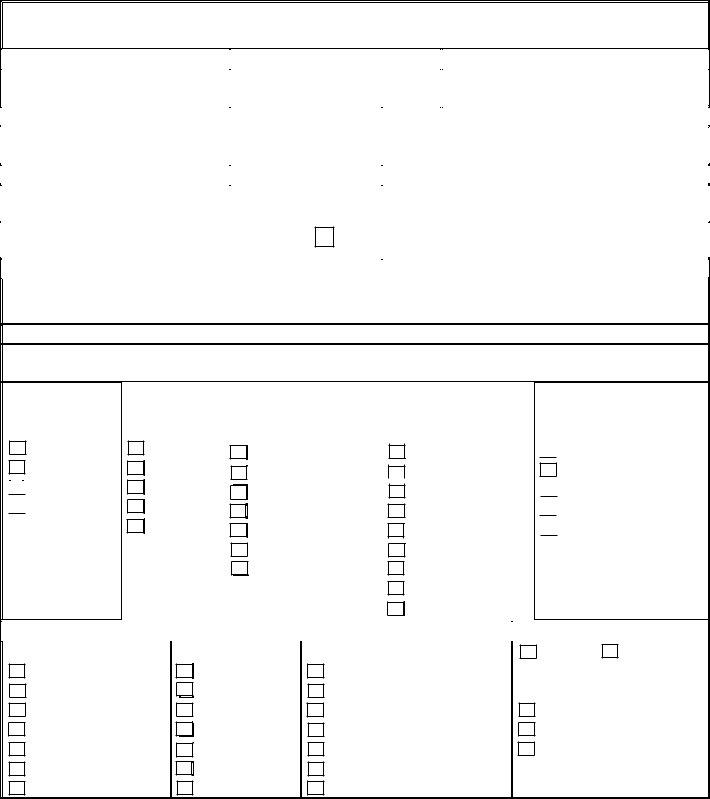
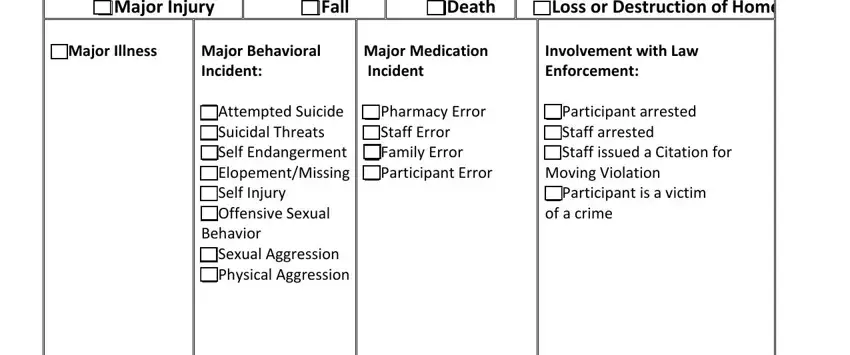
2. Specify the Incident Categories
Check the applicable categories under which the incident falls. These categories are divided into groups based on age: Adults (ages 18-59) and Elderly (ages 60 and older). Categories include abuse, neglect, exploitation, major injuries, and behavioral incidents. Remember to report any protective services allegations verbally immediately.
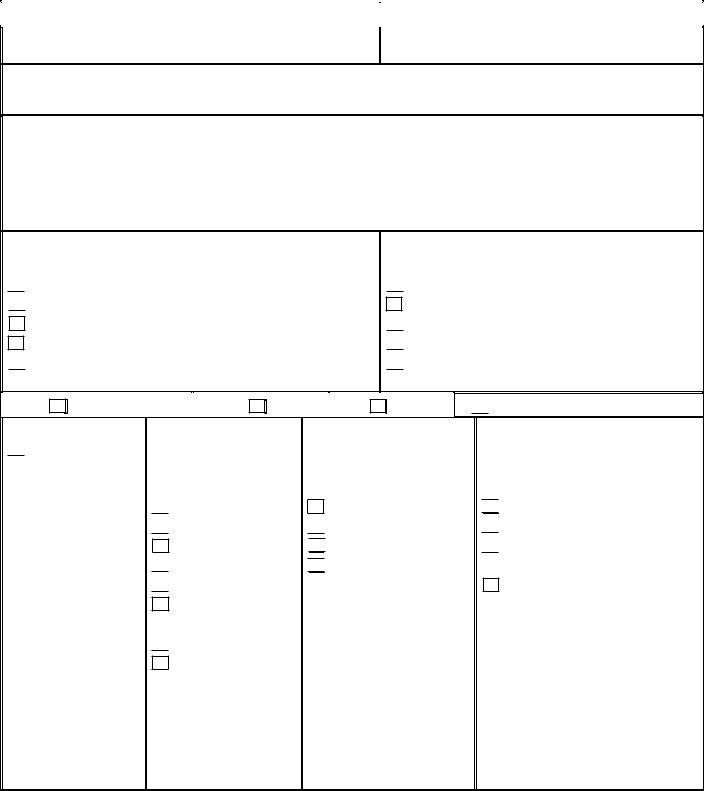
3. Detail the Event Information
Record the date and time the incident occurred and was discovered. Specify the location of the incident, such as home, community, facility, or vehicle. Notify appropriate services like Emergency Protective Services (EPS), Adult Protective Services (APS), or law enforcement, and log the dates and times of these notifications.

4. Document Health Care Admissions
Check the appropriate boxes if the participant was admitted to any healthcare facility due to the incident. These might include psychiatric hospitals, rehabilitation facilities, emergency rooms, or other relevant healthcare services.
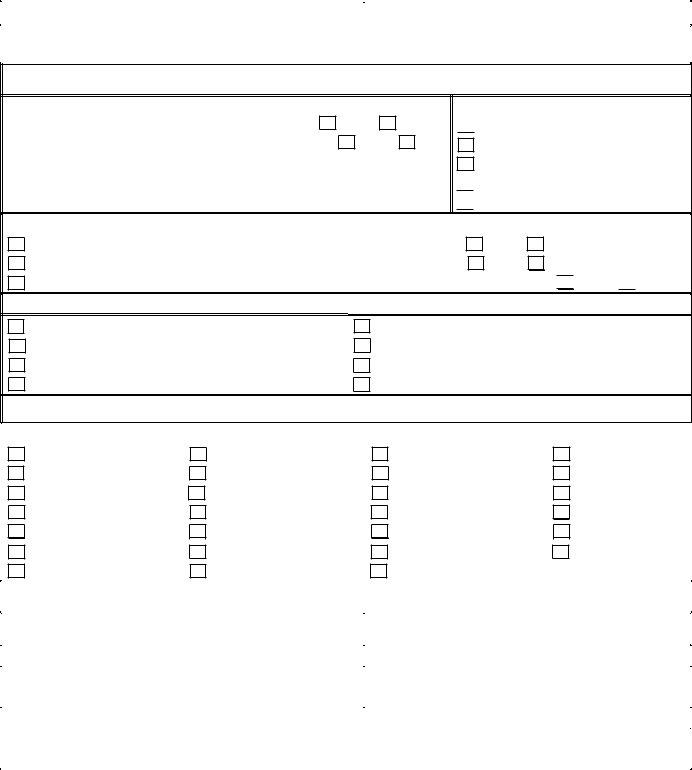
5. Write a Detailed Incident Description
Provide a comprehensive description of the incident. Include all relevant details, such as who was involved, what happened, where it took place, and how the incident unfolded. Include the agency's name and contact person if law enforcement was involved. Use additional pages as necessary, ensuring each is numbered, dated, and signed.

6. Direct Service Provider Follow-Up
Enter any follow-up actions taken in response to the incident. It might include results from medical or dental appointments, changes in medication or treatment plans, staffing changes, or adjustments to the participant’s support plan. All follow-up notes should be detailed to ensure a complete understanding of the incident's aftermath and ongoing management.