Delving into the intricacies of flowering plants, the Plant Review Worksheet offers a detailed exploration of the diversity and reproductive mechanisms within these botanical wonders. By examining the two primary methods of pollination—wind and animal—the worksheet sheds light on the intricate relationships between plants and their environments. The concept of fruit as a mature flower ovary opens up discussions on the essential roles fruits play in seed dispersal and the protection and nourishment of plant embryos. Further dividing flowering plants into categories based on the number of cotyledons, or seed leaves, the worksheet distinguishes between monocots and dicots through visual aids and descriptions. Attention is also given to the structural differences between woody and herbaceous stems, highlighting the adaptability and variety within the plant kingdom. Lifecycle classifications of annuals, biennials, and perennials offer insights into the survival strategies of flowering plants. The worksheet goes on to delve into the mechanisms of reproduction in flowering plants, particularly emphasizing the efficiency of animal pollination over wind pollination due to its lower energy demand on plants. The development of the endosperm as a food source for the developing plant embryo introduces the critical concept of double fertilization, a unique feature of angiosperms. Through labeling exercises, students are encouraged to identify key flower structures and understand their functions, reinforcing the lesson with practical engagement. The comparison between gymnosperms and angiosperms further broadens the understanding of seed-producing plants, emphasizing the diversity and complexity inherent in the world of flowering plants.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Form Name | Plant Review Worksheet Part 2 Form |
| Form Length | 4 pages |
| Fillable? | No |
| Fillable fields | 0 |
| Avg. time to fill out | 1 min |
| Other names | service review forms for interior plant service, plant notes pdf, worksheet on difference between epigeal and hypogeal germination, how a plant grows book to make |
Name: __________________________________________ Date: _________________ Period: ______
Plant Review Worksheet | Part 2
Diversity of Flowering Plants
1.What are the two ways flowering plants allow for pollination?
a.Wind
b.Animals
2.What is a fruit? Mature flower ovary
3.What is the role of fruit?
a.Seed dispersal
b.Protect & nourish plant embryo.
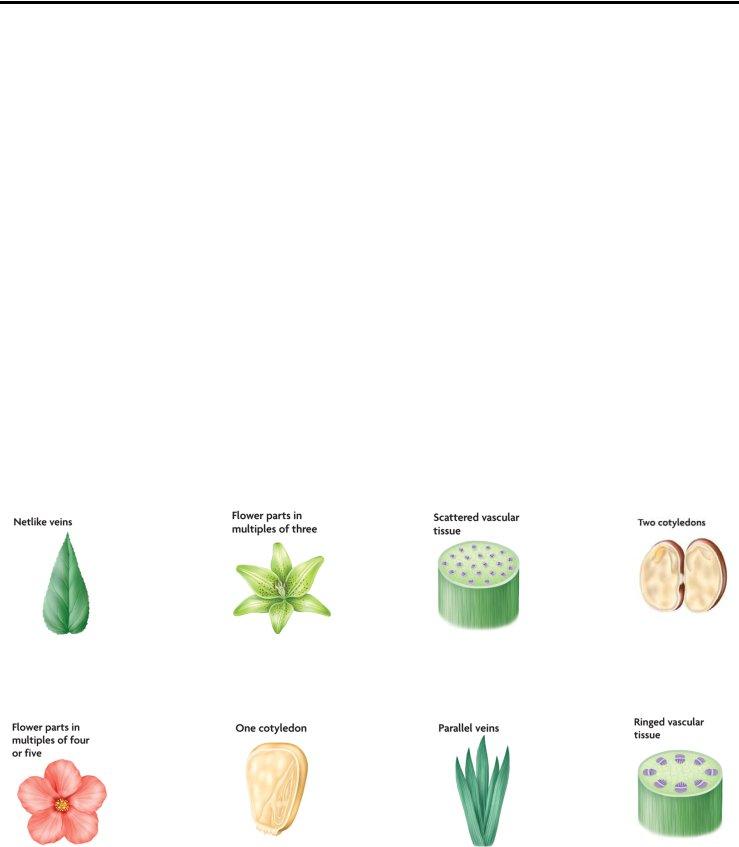
4.Botanists classify flowering plants into two groups based on their # of Cotyledons (Seed leaves)
5.For the following pictures and descriptions write “M” for monocot or “D” for dicot:
Dicot |
|
Monocot |
|
Monocot |
|
Dicot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dicot |
Monocot |
|
Monocot |
|
Dicot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.Flowering plants can also be categorized by stem type and lifespan.
7.Compare and contrast flowering plants two stem types:
Woody |
Herbaceous |
• |
High quantities of lignin |
|
• |
Don’t produce wood |
• |
Tall |
Cellulose |
• |
Lignin in lower |
• |
Stiff cell walls |
|
|
quantity |
|
|
|
||
• |
Thick cell walls |
|
|
|
• |
Dead cells |
|
|
|
8.Match the following plant life spans with their correct definition:
___b___ Plants that take 2 years to complete their life cycle.
___c___ Plants that live for more than 2 years
___a___ Plants that mature from seeds, produce flowers,
and then die all in one year.
a.Annuals
b.Biennials
c.Perennials
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
9. Answer the following questions, then CIRCLE the type of pollination that is more efficient:
a.Flowers that are small and produce large amounts of pollen are usually pollinated by?
Wind
b.Flowers that are large and produce small amounts of pollen are usually pollinated by?
Animals
c.Why is (fill in answer) Animal pollination advantageous?
Requires less energy output (pollen creation) from plant which makes it more efficient.
10.What is an endosperm? The food source for the developing plant embryo.
a.How does it form? One sperm fuses with the two polar nuclei in the plant ovary creating a triploid (3n) endosperm.
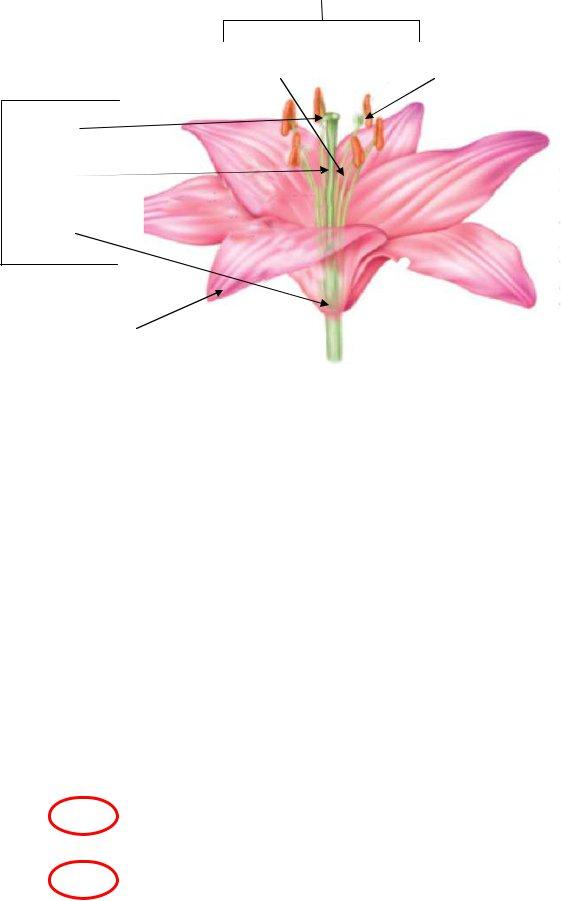
a. ___Stamen___
11. Label the flower’s structures:
b. Filament |
c. Anther |
|
e.Stigma
d.Carpel
f.Style
g.Ovary
h.Petal
12. Fill in the blanks:
The outermost layer of a flower is made of sepals which protect the flower. Just inside the outermost layer is another layer of modified leaves called petals, which can be brightly colored. Most flowers have both male and female structures. A stamen is the male structure of a flower and it has a stalk called a filament. This stalk supports an anther which produces the male gametophytes: pollen grains. The innermost part of the flower is the female structure called the carpel. Each female structure has three parts. The stigma is the top part that is sticky and holds the pollen grains when they land there. The style is the tube that leads from the top part of the carpel to the base of the flower. This base is called the ovary, and it is where female gametophytes are produced.
13. Answer the following questions about the angiosperm’s male gametophyte:
a. The anthers produce pollen grains which divide by meiosis. This means the spores are:
(circle one) haploid or diploid.
b. The spores divide again, but by mitosis. This means the spores are: (circle one) haploid or diploid.
c. How many cells make up a single pollen grain? THREE!
14.Place the steps of the angiosperm life cycle in order, from the step started for you: 1 Pollen lands on the stigma = pollination.
3_ The sperm travel down the pollen tube.
6_ Each ovule becomes a seed and the surrounding ovary grows into a fruit.
2_ One haploid cell of pollen grain forms the pollen tube. The other haploid cell forms 2 sperm nuclei.
5_ A triploid (3n) endosperm forms.
7_ Seeds get dispersed.
8_ Seed germinates, and the cycle starts over.
4_ One sperm fertilizes the egg and the other joins with the 2 polar nuclei.
15.What is double fertilization?
When one sperm fertilizes the egg = zygote, and the other sperm forms with the two polar nuclei = triploid enderosperm,
16.Compare and contrast the following types of seed producing plants:
Gymnosperms |
Angiosperms |
• Cone bearing |
|
• Seed enclosed in fruit |
|
• Trees |
Woody |
• |
Flowers |
• Seeds not enclosed in fruit |
Endosperm |
• |
Herbaceous |
• Endosperm created for |
Fertilization |
• |
Endosperm only |
each ovule |
without H2O |
|
created when egg is |
|
|
|
fertilized. |