Form 1040-ES, titled “Estimated Tax for Individuals,” is a form used by individuals to pay estimated tax on income that is not subject to withholding. This includes earnings from self-employment, interest, dividends, rents, and other forms of income. The form provides worksheets to help taxpayers estimate their tax liability for the year and determine the amount of their quarterly estimated tax payments. It is especially relevant for freelancers, independent contractors, and small business owners who do not have taxes automatically withheld from their income.
The purpose of Form 1040-ES is to facilitate the quarterly payment of taxes, which helps taxpayers avoid underpayment penalties at the end of the tax year. The IRS requires taxpayers to make estimated tax payments if they expect to owe at least $1,000 in tax for the year after subtracting withholdings and credits and if they expect their withholdings and credits to be less than smaller of 90% of the tax to be shown on the current year’s tax return, or 100% of the tax shown on the prior year’s tax return. This form is crucial for ensuring taxpayers remain compliant with IRS regulations by spreading their tax liability throughout the year.
Other IRS Forms for Self-employed
What you need to file your taxes varies depending on your situation. Check what IRS forms are often filled out by our users along with the standard tax return form for individual taxpayers.
Filling Out IRS Form 1040-ES
Completing the 1040-ES report is a straightforward and intuitive process. Still, it might be challenging for some declarants, as the paperwork consists of several parts. Below is the list of components compulsory for the taxpayers to accomplish:
- Estimated Tax Ledger
- Tax Rate Schedules
This section is needed to calculate the estimated tax.
- Self-Employment Tax and Deduction Ledger
The worksheet is used to specify units 1 and 9 of the Estimated Tax Ledger.
- Record of Estimated Tax Payments
- Four 1040-ES Vouchers
The compilation also includes a vast instruction section.
Here, you will find a clear directive for preparing and serving the 1040-ES report and related payments.
1. Download an Up-to-Date PDF File
We empower you to use our advanced software to generate and download the respected 1040-ES form.
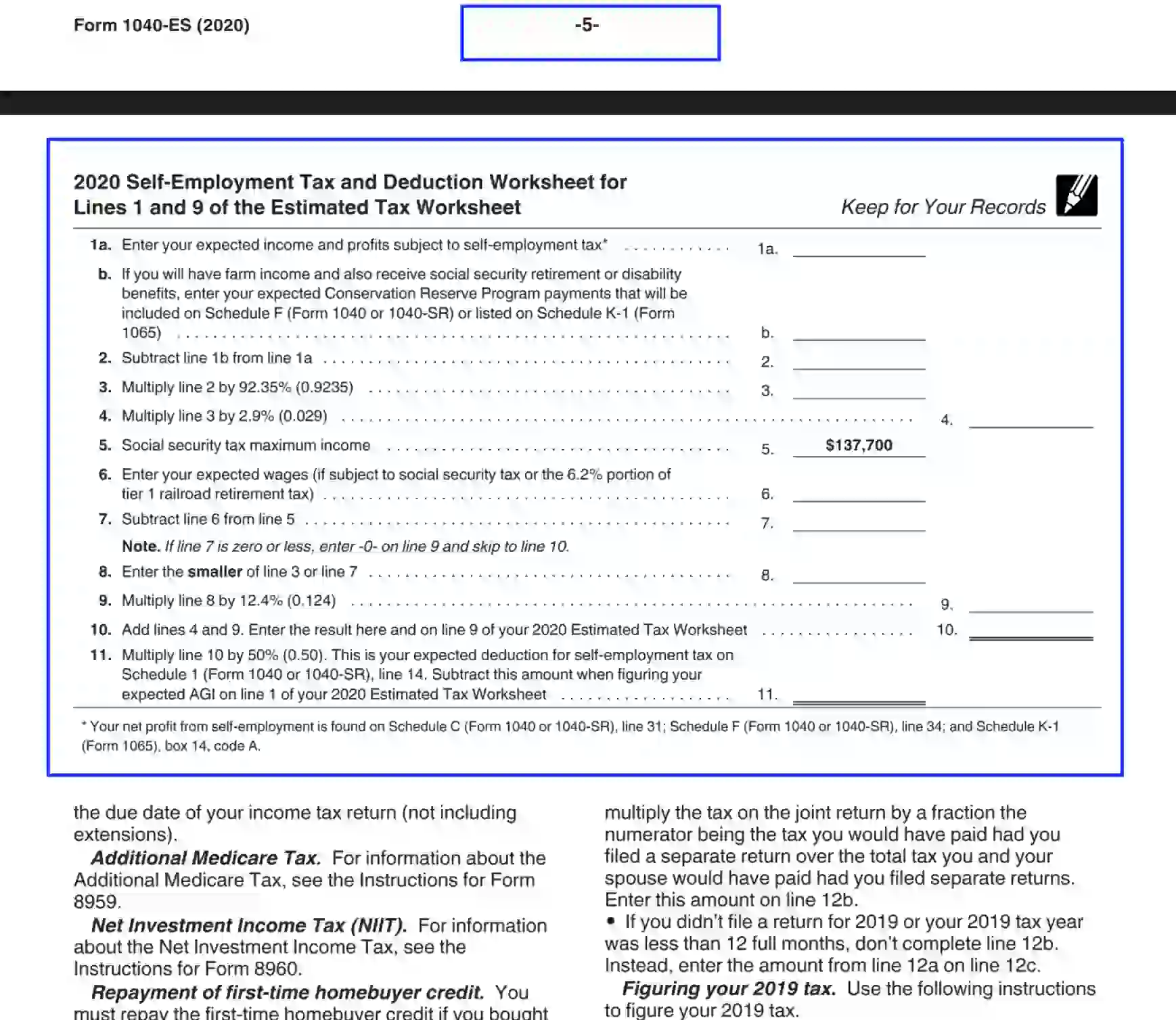
2. Prepare the Self-Employment Tax and Deduction Ledger
Proceed to page “6” to accomplish the worksheet. Study the instructions carefully to submit the needed data in the Self-Employment Tax Deduction ledger. Specify the expected amounts next to each unit and provide the calculations required:
- Expected profits that are subject to self-employment charges.
- Conservation Reserve Program amounts (applicable for those who hold farm profits and social benefit refunds).
- Wages you suppose to get that is subject to SS tax or railroad retirement rate.
- Calculation requested in units 2-4 and 7-11.
The SS Tax Maximum profit is already committed to the form and equals 137,700 USD.
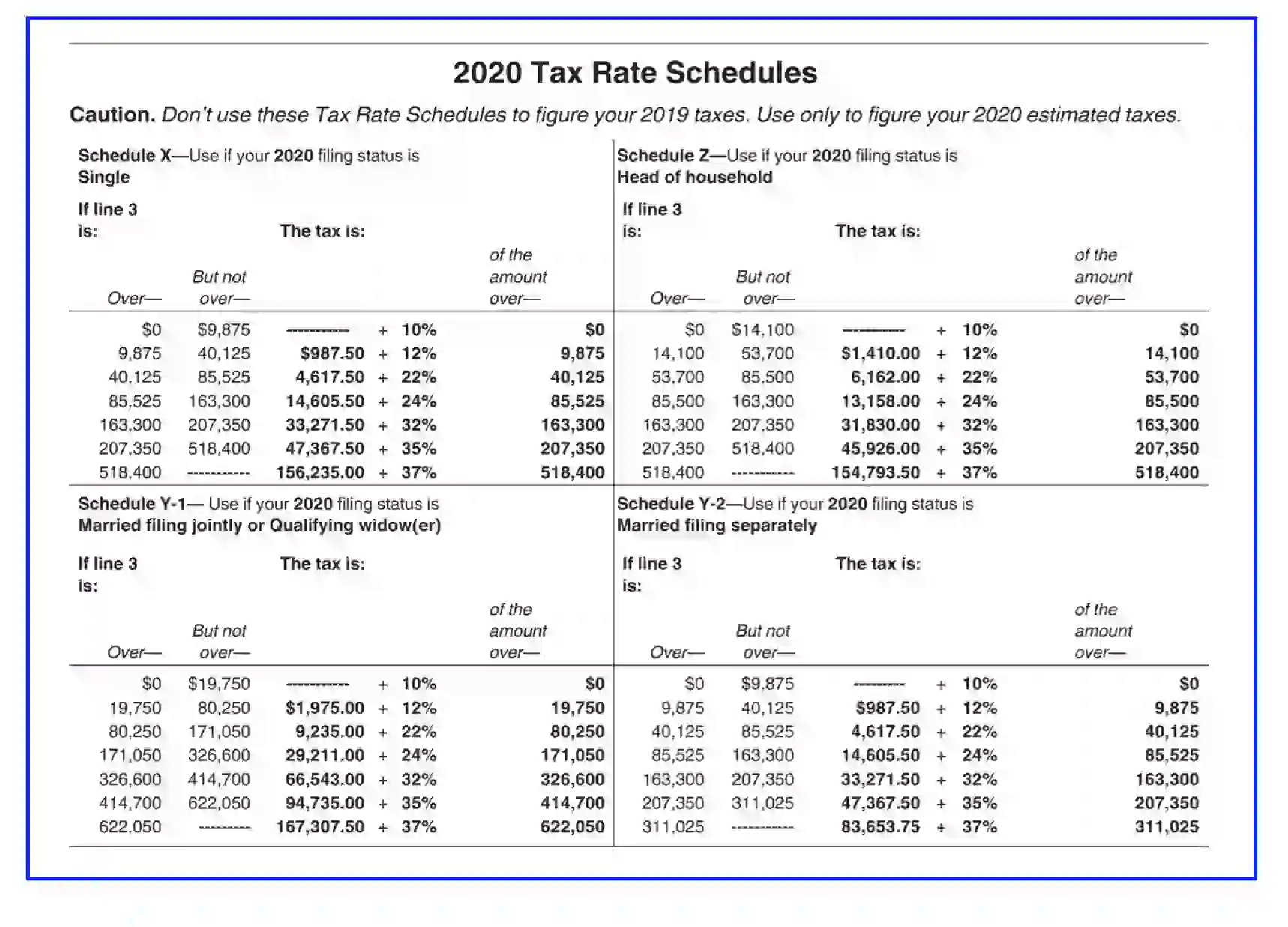
3. Complete the Estimated Tax Ledger
Begin completing the worksheet on page “8” after you read the guidelines on page “5-6.” The Estimated Tax ledger consists of 15 units and blank space that you can utilize to provide the answers next to each question.

You should turn to the Tax Rate Schedules on page “7” to estimate and calculate the amount in section “3” and “4.”
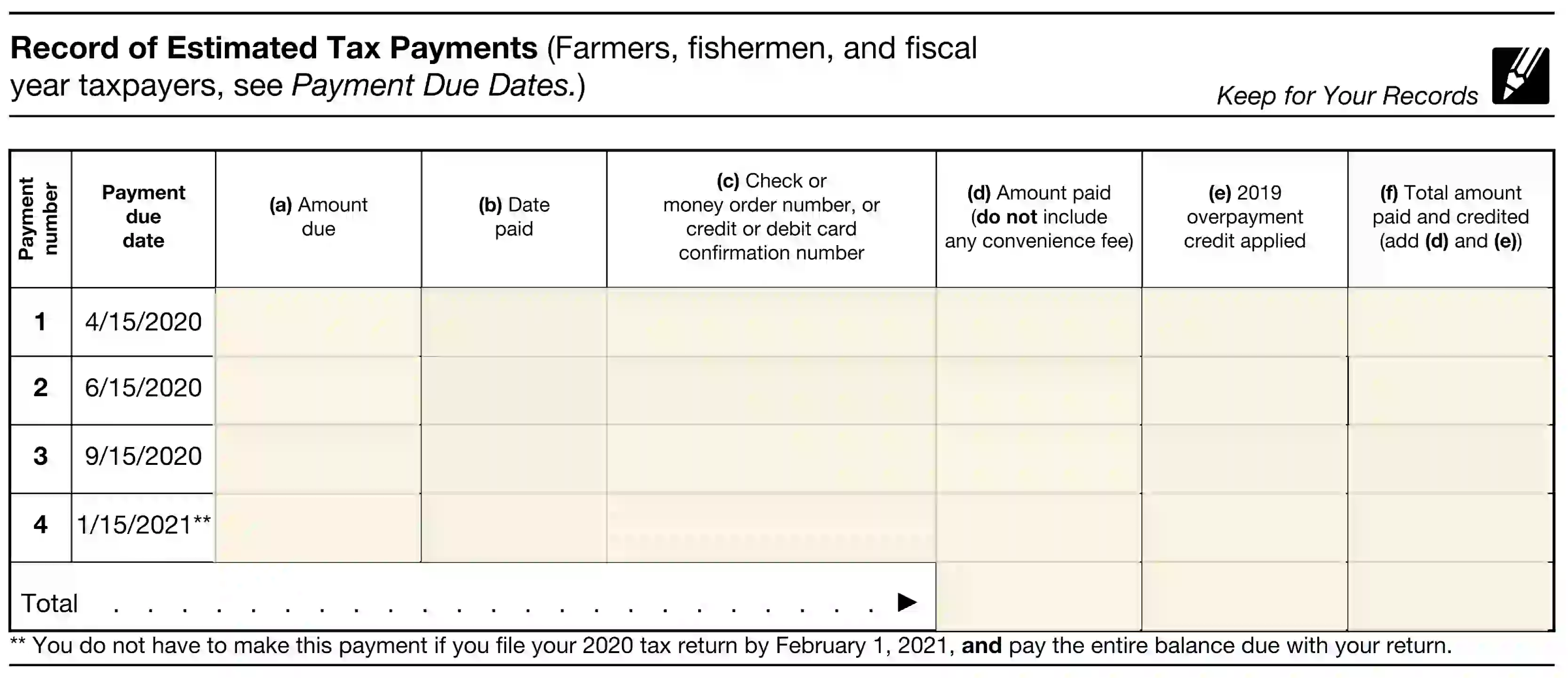
4. Prepare the Record for Estimated Tax Payments Section
Completing this section relies on results submitted in unit 14 (a-b) of the Estimated Tax sheet. If, after the calculations, your amounts satisfy the requirements of the “Yes” boxes, you are not obliged to provide the Estimated Tax Payments data.

However, if your amounts exceed 1,000 USD, follow the instructions, and complete the Estimated Tax Payments Record. The table contains five horizontal lines specifying the due date period and the total. To meet the demands of the worksheet, you need to enter the following info:
- Amount due
- Date of payment
- Confirmation info proving the payment
- Funds paid
- Info, if you paid with the previous year’s overpayment credit.
- Total
5. Render the 1040-ES Voucher
Select the appropriate type of voucher depending on the due date you provide payments for. Consider the info at the upper right corner of each voucher to adjust the needed alternative.
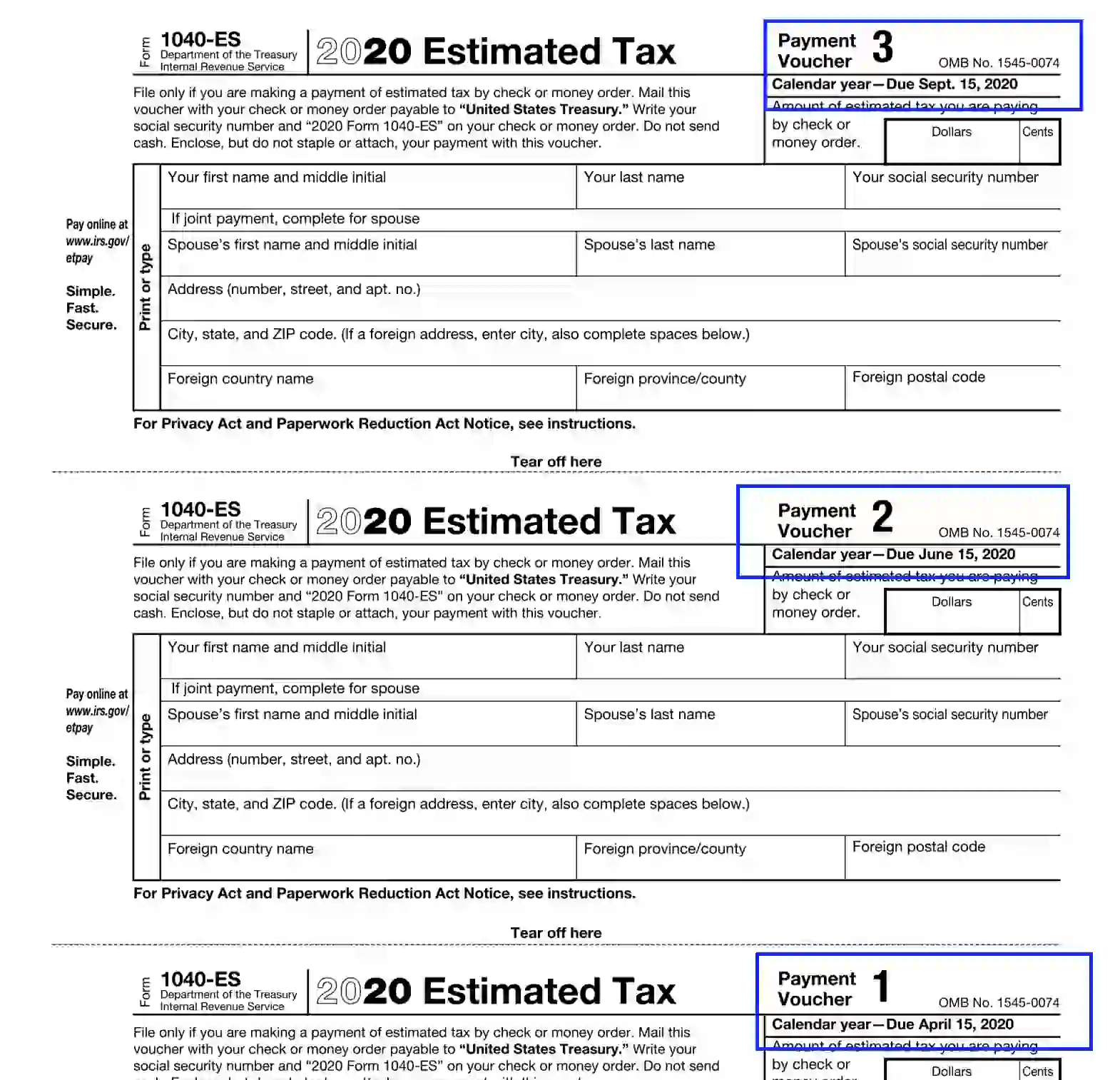

Once you have chosen the voucher type, you should enter the following data:
- Enter the amount in a dollar-cent format; for example, 100.00 USD.
- The declarant’s first and last name and middle initials
- SSN
- Full address, including the street and apartment (room) number, city, state, and ZIP.
- If you provide the data jointly, please, include the spouse’s name, SSN, and address using your model.
- Should you reside in a foreign country, submit the full location and postal code.
The voucher should be served to the U.S. Treasury and only if the declarant uses money order or check payment methods. Enter the declarant’s name, SSN, and “[Calendar Year] 1040-ES” on the check or money order. Also, it is vital to submit but not staple or glue the payments with the voucher.f
