Form 5329 is an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) attachment used to report additional taxes on withdrawals or contributions to certain tax-advantaged retirement accounts. These accounts include IRAs, traditional 401(k) plans, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), and Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs).
Essentially, it’s a form you file if you did something with your retirement savings that triggered an IRS penalty. Common reasons for needing Form 5329 include taking an early distribution from your IRA or exceeding contribution limits to your IRA or HSA. The form helps you calculate any taxes or penalties owed and allows you to attach it to your tax return.
Instructions For This Form
Filling out any tax return requires an understanding of financial subtleties, mathematical calculations, and time. Do not postpone this matter until a later date not to find yourself in a force majeure situation. Carefully read the step-by-step guide, check the entered data several times, and sign it.
Fill out basic data
The tax structures require complete information about you. Enter your first and last name, residential address, and social security number. If you are a foreigner, also write information about your country. By the way, if you only owe an additional tax of ten percent of the amount of the early distributions, enter this information on Form 1040 without filling out this one.
Qualify early distributions
So, the first part of the form refers to the additional tax of early distribution. If you fall into this category, the penalty will be ten percent. However, there are cases when this type of tax does not apply.
For instance, if there were qualified natural disasters and a coronavirus. Secondly, you make a qualified allocation for the birth or adoption of a child of up to $ 5 000. In this case, attach a statement with information about your child. Also, it does not include distribution from a savings or traditional account and a planned rollover. Fill out the first part, specifying the exact amounts.

Enter other distributions
The second part of the tax return does not differ in structure from the first. However, this section applies to additional taxes on certain distributions to educational and active accounts. Payments from this account are not part of the income if it related to the death of the beneficiary:
- to the property of this person
- to the heirs of this beneficiary
- outstanding obligations
Enter all valid amounts and proceed to the following questions.

Enter excess contributions
The Tax Service requests information about excess contributions, so specify all data in the third section. If you paid more than you were supposed to in 2020, you owe this tax. At the same time, you may also avoid excess taxes.
Enter the difference in the amounts. Fill in any information about the contributions by the requirements. By the way, even if you filed your tax return on time without withdrawing the excess contributions, you may do so only six months after the deadline for submitting your documents.

If the third part of the form refers to traditional accounts, the fourth part describes other qualified plans. Consider the difference in amounts when calculating tax payments. In some cases, it may play in your favor. In line 20, enter the amount and any qualified distributions.
By the way, you may withdraw part or all of the excess contributions for 2020 if you do the following:
- you get the money within the prescribed period, including the extension of the tax return
- you withdraw any income on your contributions and add them to the gross income
If you have withdrawn the balance from your individual retirement account, do not enter the smaller amount. Use our form-building software to fill out the tax return faster.

Cover additional issues
All other sections of this tax return have the same structure and require mathematical calculations. The difference is only in understanding the types of qualified accounts. So check out the key concepts below.
Traditional accounts are a type of individual retirement account that ensures the growth of your invested funds. It means that you will not pay capital gains taxes on investment profits, dividends, or interest on the account. You may buy and sell a wide range of assets in a traditional account.
The Coverdell ESA is a savings account that allows you to make up to $ 2 000 per child per year in after-tax contributions in the child’s name. The contribution of funds is made only in cash, which will grow due to the deferred payment of taxes. This allowance applies to qualified expenses for higher, primary, and secondary education.

The Archer MSA is a medical savings account accompanied by a high deductible health insurance plan. These funds help the owner pay for expenses before reaching the plan’s deductible and fees for qualified expenses that the scheme does not cover.
Fill in these items according to your needs, indicating reliable information about the accounts. If you have any difficulties, contact a tax specialist for help, who will explain all details to you.
As a rule, an able account means a universal plan that allows you to save money on caring for your disabled child or a loved one. At the same time, no other benefits disappear. If your child or loved one has a disability, then taking care of them requires a financial investment. You need to pay for medical care, care, and pills. That is why it is better to use this account.

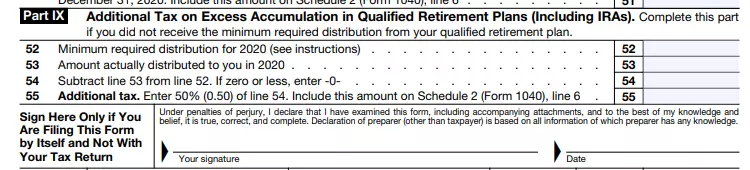
A qualified retirement plan meets the requirements of the USA laws for tax benefits. They are usually offered through an employer and allow for pre-tax contributions and tax-deferred growth. It is the best option for creating retirement savings.
After filling out this part, be sure to sign the tax return and put the date. Your signature is a sign of your consent and a confirmation of your responsibility.
Use paid assistance
In case of difficulties and other circumstances, the taxpayer has the right to use the service of a paid compiler. This person fills out the entire tax return and this section of the form. The paid compiler provides information about himself, including his first name, last name, address, and phone number. At the same time, you pay for this service.

